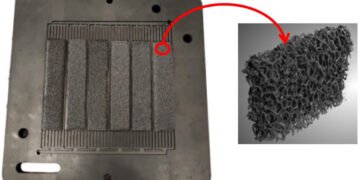
A research team from the Department of Energy Engineering at the University of Seville has developed an experimental research focused (A new bio-inspired PEM fuel cell with graphene sponge) on the design of a bio-inspired PEM fuel, cell which included graphene porous sponge inserts. The model they have obtained has reached a maximum power which is up to 6.0% higher than the design they took as a reference (“Experimental and numerical Investigation on the design of a bioinspired PEM fuel cell“).
Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFC) are electrochemical devices that directly convert the chemical energy of fuels such as hydrogen into electricity, with high efficiency and creating only water as a by-product. The geometry of the channels in the bipolar plate through which the reactants are distributed has a considerable impact on the performance of the fuel cell.
Bipolar plate designs based on nature-inspired structures such as leaves, lungs or sponges have been successfully explored so far but have not yet reached their full potential.
With the aim of investigating new designs with improved performance, this work presents an experimental analysis of a novel bioinspired design of the channels of a PEMFC.
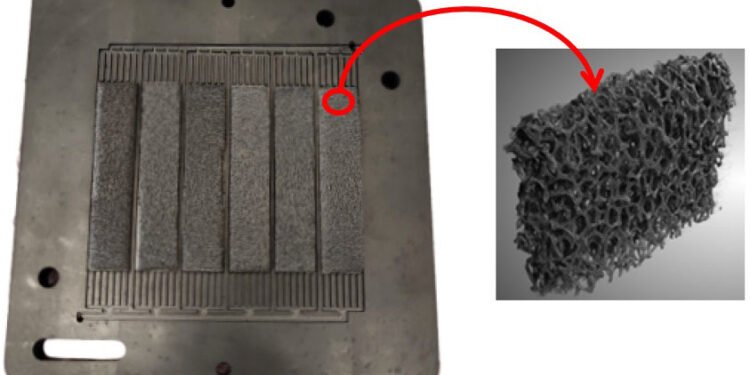
Starting from a Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) analysis of the flow of different initial biomimetic designs, the one that presented the best performance in terms of reactant distribution, which includes insertions of porous material in the central area of the plate instead of channels, was selected, manufactured and experimentally tested.
The results of the new biomimetic design were analyzed and compared with a parallel coil model, which was taken as a reference, indicating that the proposed new design is especially suitable for improving fuel cell water management in high humidity conditions. reactants, achieving up to 6.0% higher peak power compared to the reference design.
News Source: nanowerk