Dust is a common thing in life, and it’s not just a daily annoyance – it can get into machines and equipment, causing loss of performance or breakdown. Researchers from the University of Texas at Austin have teamed up with North Carolina company Smart Material Solutions Inc. to create a new system to prevent dust from sticking to the surface. The result is the ability to make many different types of objects (Anti-dust technology paves the way for self-cleaning) dust-resistant, from airplanes to skylights to house windows.
Authentication is published in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.
“Our showing that this is the one to suck,” the Walker section of the engineering and the mainline. “Those particles can’t stick to the surface, so they are removed using only the force of gravity.”
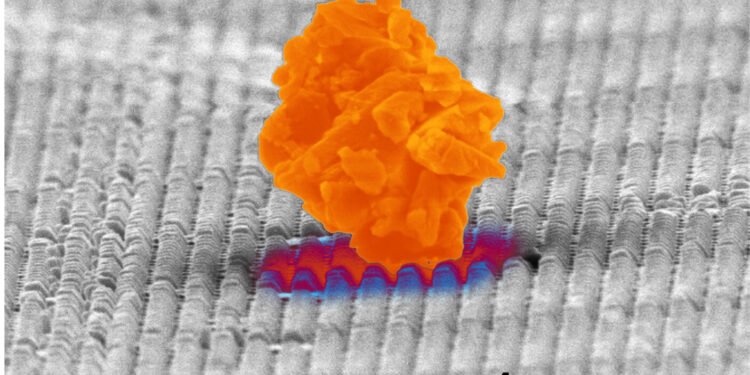
In a test, the researchers piled moon dust on top of their surfaces, then turned each surface on its side. The result: only about 2% of the surface is still dust, compared to more than 35% of the surface is similar and flat.
The researchers said that this finding comes down to what the human eye cannot detect. In the experiments, the team changed the geometry of the flat surface to create a solid nanoscale structure of pyramid-like material. These sharp edges prevent dust particles from sticking to the material, instead of sticking to each other and rolling over the surface of the material by gravity.
These structures provide a passive solution, which means they do not require additional power or equipment to remove sand. Compare this to a more labor-intensive solution such as a car cover that requires the use of an air-tight seal and a liquid to clean the dust.
The research was funded by a grant from NASA’s Small Business Research Program, so the first application focused on space technology. Space dust is particularly problematic because of the high risk of anything becoming in this environment, and conditions that make it difficult to clean the sand. The dust caused chaos in the Apollo missions and caused the crash of the Mars rover.
“There’s not much you can do about moon dust in the sky – it sticks to everything and there’s no way to clean it or spray it,” Samuel said. Lee, the senior author is an undergraduate researcher in Chang’s group. “Dust in the skies of Mars rovers could cause them to crash.”
This technology can also have a big impact on the world. This can prevent the sunroof from collecting dust and fading over time. It can protect glass windows and one day even digital screens like cell phones and televisions.
Anti-dust technology has been around for decades, but it hasn’t gained much traction outside of the lab because of major problems. The researchers used a manufacturing concept called nanocoining and nanoimprinting, which documented the principles and elements of the modern style of how newspapers and photographs were produced in many places in the 1800s.