How do you identify the components of an unknown object, such as a meteorite? X-ray fluorescence can be used to detect many things, by using X-rays to increase the sample and analyze the spectrum they emit and can detect many things at the same time. For this reason, X-ray fluorescence analysis has been used to determine the level of toxic heavy metals in soil. Current X-ray fluorescence detection methods take about 10 minutes to accurately detect objects, so new methods are needed that can measure large quantities (Bayesian analysis dramatically reduces X-ray fluorescence analysis time!) or quickly take multiple measurements of unknowns.
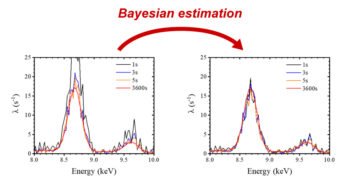
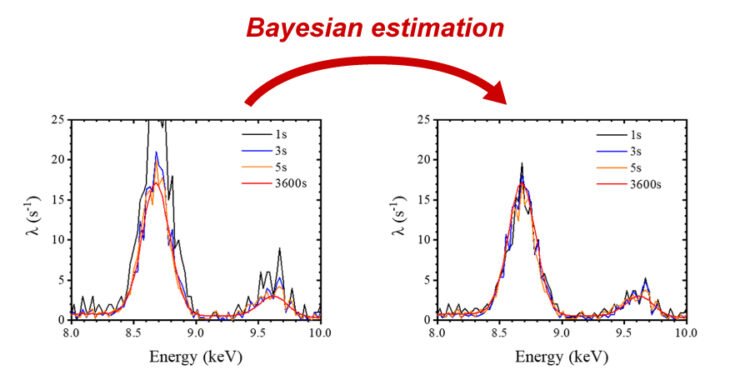
A joint research team, including Dr. Tsugufumi Matsuyama, Professor Kouichi Tsuji and Masanori Nakae, a second Masters student at Osaka Metropolitan University‘s Graduate School of Engineering, and researchers from the Japanese Atomic Energy Agency, developed a new method that applies Bayesian planning. X-ray fluorescence analysis, the team succeeded in reducing the measurement time of the X-ray fluorescence spectrum per point, from 7 seconds to 3 seconds, reducing the time required to obtain the results of the analysis that are less different and the spectra obtained from measurements. Standard sample cup for one hour from 4 seconds. For example, when doing an elementary distribution, up to 10,000 points can be taken, rather than a small area, depending on the sample. Therefore, reducing measurement time per second by 4 seconds can reduce total measurement time by 40,000 seconds, or about 11 hours, when creating an elementary distribution.
Dr Matsuyama said: “We have successfully integrated research into computer science, using Bayesian inference and X-ray fluorescence analysis. If we can perform a rapid analysis in a non-destructive way without the need to contact the sample, this method can be popular in many areas, such as the analysis of industrial products or is the waste that is transported in the conveyor belt, and the monitoring of the chemical reaction in progress. . “