Electronic tongue uncovers AI inward thoughts: Researchers created an electronic tongue that can recognize different fluid tests utilizing manufactured insights. When inquired to characterize its claim evaluation parameters, the AI might more precisely decipher the information produced by the electronic tongue.
A as of late created electronic tongue is able of recognizing contrasts in comparable fluids, such as drain with changing water substance; assorted items, counting pop sorts and coffee mixes; signs of decay in natural product juices; and occurrences of nourishment security concerns. The group, driven by analysts at Penn State, too found that comes about were indeed more precise when fake insights (AI) utilized its possess appraisal parameters to translate the information produced by the electronic tongue.
The analysts distributed their results (Oct. 9) in Nature.
According to the analysts, the electronic tongue can be valuable for nourishment security and generation, as well as for restorative diagnostics. The sensor and its AI can broadly identify and classify different substances whereas collectively evaluating their individual quality, genuineness and freshness. This evaluation has moreover given the analysts with a see into how AI makes choices, which seem lead to superior AI advancement and applications, they said.
“We’re attempting to make an manufactured tongue, but the handle of how we encounter diverse nourishments includes more than fair the tongue,” said comparing creator Saptarshi Das, the Ackley Teacher of Designing and teacher of designing science and mechanics. “We have the tongue itself, comprising of taste receptors that associated with nourishment species and send their data to the gustatory cortex — a natural neural network.”
The gustatory cortex is the locale of the brain that sees and deciphers different tastes past what can be detected by taste receptors, which fundamentally categorize nourishments by means of the five wide categories of sweet, acrid, sharp, salty and savory. As the brain learns the subtleties of the tastes, it can way better separate the nuance of flavors. To falsely copy the gustatory cortex, the analysts created a neural arrange, which is a machine learning calculation that imitates the human brain in surveying and understanding information.
“Previously, we examined how the brain responds to diverse tastes and mirrored this prepare by joining diverse 2D materials to create a kind of outline as to how AI can prepare data more like a human being,” said co-author Harikrishnan Ravichandran, a doctoral understudy in designing science and mechanics prompted by Das. “Now, in this work, we’re considering a few chemicals to see if the sensors can precisely identify them, and besides, whether they can distinguish diminutive contrasts between comparable nourishments and perceive occasions of nourishment security concerns.”
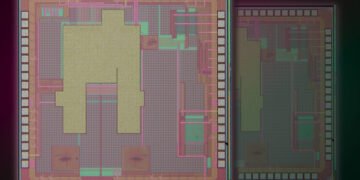
The tongue comprises a graphene-based ion-sensitive field-effect transistor, or a conductive gadget that can identify chemical particles, connected to an manufactured neural organize, prepared on different datasets. Basically, Das famous, the sensors are non-functionalized, meaning that one sensor can distinguish diverse sorts of chemicals, or maybe than having a particular sensor devoted to each potential chemical. The analysts given the neural arrange with 20 particular parameters to evaluate, all of which are related to how a test fluid interatomic with the sensor’s electrical properties. Based on these researcher-specified parameters, the AI seem precisely identify tests — counting watered-down milks, diverse sorts of soft drinks, mixes of coffee and numerous natural product juices at a few levels of freshness — and report on their substance with more prominent than 80% precision in almost a minute.
“After accomplishing a sensible exactness with human-selected parameters, we chosen to let the neural arrange characterize its possess figures of justify by giving it with the crude sensor information. We found that the neural arrange come to a close perfect deduction exactness of more than 95% when utilizing the machine-derived figures of justify or maybe than the ones given by humans,” said co-author Andrew Pannone, a doctoral understudy in designing science and mechanics prompted by Das. “So, we utilized a strategy called Shapley added substance clarifications, which permits us to inquire the neural organize what it was considering after it makes a decision.”
This approach employments diversion hypothesis, a decision-making handle that considers the choices of others to foresee the result of a single member, to relegate values to the information beneath thought. With these clarifications, the analysts may switch build an understanding of how the neural arrange weighed different components of the test to make a last assurance — giving the group a see into the neural network’s decision-making handle, which has remained to a great extent misty in the field of AI, agreeing to the analysts. They found that, instep of basically surveying person human-assigned parameters, the neural arrange considered the information it decided were most critical together, with the Shapley added substance clarifications uncovering how imperative the neural arrange considered each input data.
The analysts clarified that this appraisal may be compared to two individuals drinking drain. They can both recognize that it is drain, but one individual may think it is skim that has gone off whereas the other considers it is 2% that is still new. The subtleties of why are not effortlessly clarified indeed by the person making the assessment.
“We found that the organize looked at more unpretentious characteristics in the information — things we, as people, battle to characterize properly,” Das said. “And since the neural arrange considers the sensor characteristics comprehensively, it mitigates varieties that might happen day-to-day. In terms of the drain, the neural organize can decide the shifting water substance of the drain and, in that setting, decide if any pointers of debasement are important sufficient to be considered a nourishment security issue.”
According to Das, the tongue’s capabilities are constrained as it were by the information on which it is prepared, meaning that whereas the center of this ponder was on nourishment evaluation, it seem be connected to therapeutic diagnostics, as well. And whereas affectability is imperative no matter where the sensor is connected, their sensors’ vigor gives a way forward for wide sending in distinctive businesses, the analysts said.
Das clarified that the sensors don’t require to be absolutely indistinguishable since machine learning calculations can see at all data together and still create the right reply. This makes for a more down to earth — and less costly — fabricating process.
“We figured out that we can live with imperfection,” Das said. “And that’s what nature is — it’s full of defects, but it can still make vigorous choices, fair like our electronic tongue.”
Source: By Ashley WennersHerron, Penn State