Bacteria with a built-in compass
by Christine Möller
Some bacteria are miniature masters of navigation: A built-in “compass” made of magnetic nanoparticles helps them to reliably find the optimal habitat. Researchers at the University of Basel have now unlocked the magnetic properties of individual bacteria — an important step toward harnessing the potential for technology, environmental research and medical applications.
Some bacterial species possess an astonishing ability: They use the Earth’s magnetic field to orient themselves. To better understand this mechanism, the team led by Argovia-Professor Martino Poggio from the Swiss Nanoscience Institute and the Department of Physics at the University of Basel took a closer look at the “magnetotactic” bacterium Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense.
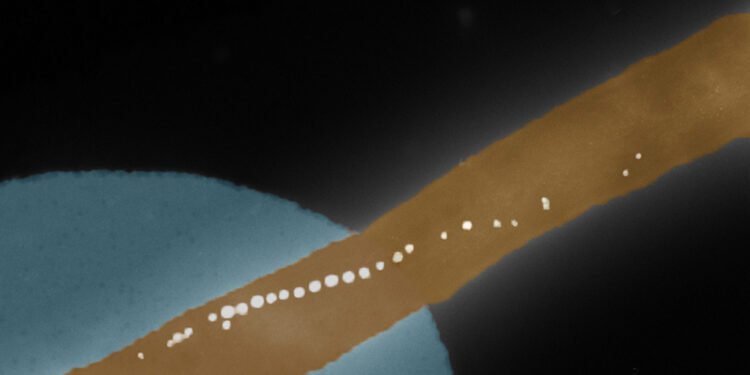
Inside this bacterium is a chain of magnetic nanoparticles known as magnetosomes. These act like a biological compass and allow the bacterium to align with the Earth’s magnetic field.
In their natural habitat, bodies of water or moist sediments, this compass helps the bacteria to advance in a systematic manner when searching for the optimal living conditions. Without this orientation, their movements would be more random, requiring greater time and energy to locate optimal oxygen levels, for example.
The potential applications of these bacteria are considerable. For instance, they could be used in medicine as magnetically controllable “microrobots” for the targeted delivery of drugs. They could also be applied in wastewater treatment, with bacteria absorbing heavy metals and then being easily removed from the water using a magnet.
A single bacterium in focus
A precise understanding of the bacteria’s magnetic properties is essential, however, before such applications become possible.
To this end, the researchers from Basel University collaborated with microbiologist Professor Dirk Schüler from the University of Bayreuth to examine the magnetic particles of a single bacterium. This poses a major technical challenge because the magnetism of an individual magnetosome chain is extremely weak. Most previous studies were limited to investigating ensembles of bacteria. However, the interdisciplinary research team has now succeeded in measuring how the magnets within a single bacterium interact under the influence of an external magnetic field. The results were recently published in the scientific journal Physical Review E.
“We first attached a single bacterium to an extremely thin cantilever and measured its vibrations in magnetic fields,” explains Mathias Claus, first author of the study and a doctoral student at the SNI PhD School. “From tiny changes in the vibration frequency, we were able to infer how strongly magnetic the bacterium is and how stable its magnetic orientation remains.”
In addition to these highly sensitive magnetometry measurements, the team also carried out electron microscopy analyses and computer simulations. They were able to determine the magnetic strength of the chain precisely and confirm that the strength is sufficient for the bacterium to align parallel to the Earth’s magnetic field under natural conditions and thus move in a directed manner. “Very strong magnetic fields can, however, influence this alignment and thereby disrupt the bacteria’s orientation. This is an important aspect for potential technical applications, such as controllable microrobots,” adds Dr. Boris Gross from the Poggio team, who initiated and led the project.
Interestingly, when the magnetic field was reversed, individual magnets or small groups suddenly switched their direction, as confirmed by the simulations. Yet this poses no risk for bacteria in a lake: the Earth’s magnetic field is not strong enough and, unlike the bacterium studied, they are not fixed to a cantilever. They simply continue to rotate until they are aligned once again with the magnetic field — before such a reversal could even occur.
Source: University of Basel