A group of researchers has developed a new acoustic waveguide based on the mathematical theory of topology, which will lead to a reduction in energy consumption in many electronic devices.
Details of their new findings were published in the journal Applied Physical Review on January 3, 2023.
As the name suggests, surface wave (SAW) is a type of sound wave where the amplitude of the vibration is focused on the surface of the object. SAW can be excited and find that the piezoelectric material, the crystal can generate electricity when it is compressed or vibrated. Electronic devices, known as SAW devices, use it and provide filtering and frequency monitoring in common electronic devices such as mobile phones and touch screens. But one of the disadvantages of SAW devices is that they consume a lot of power, which reduces battery life.
The team, consisting of Yoichi Nii and Yoshinori Onose from Tohoku University‘s Materials Research Institute, developed air conditioning as a solution to this problem.
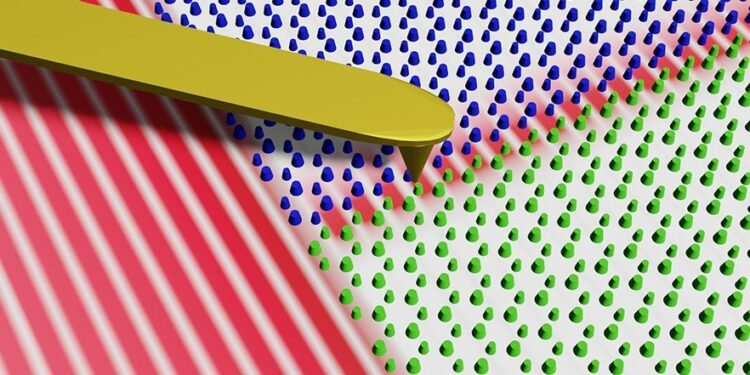
Waveguides are devices that transmit or guide waves in a vacuum. Topological waveguides are a recent development that reduces energy consumption and allows waves to be manipulated in unique ways. The topological structure of the wave path of the group reduces power consumption and can greatly extend the battery life of our phones and other electronic devices.
This waveguide also has the added advantage of being easy to fabricate and compatible with existing SAW device technology, Nii explains, “The implementation of our waveguide involves simply creating a nano-sized pillar pattern on a piezoelectric substrate.
” Wave guidance could lead to new advances in quantum technology. “SAW-based technologies have also attracted the attention of researchers exploring ways to push the boundaries of quantum computing,” Nii adds.