Quantum computers promise to perform some tasks that would be impossible even with the world’s most powerful supercomputer. In the future, scientists plan to use quantum computing (The device can be connected in parallel using a new mathematical algorithm) to model material systems, manipulate quantum chemistry, and improve complex operations, with potential implications ranging from finance to medicine.
However, achieving this promise requires durable and flexible hardware. One of the challenges in building a large-scale quantum computer is that researchers must find a good way to connect the quantum information – separate small processing units in the computer. Because quantum computers are very different from classical computers, the technique used is to directly translate electronic information into quantum devices. However, one requirement is clear: whether through classical or quantum communication, the information being carried must be transmitted and received.
To achieve this, MIT researchers have created a computational center that will enable high-speed communication between quantum operators. In a work published today in Nature Physics, MIT researchers demonstrate the first step, the determination of single photons – carriers of information – in a user-defined direction. Their method ensures that quantum information travels in the correct direction more than 96% of the time.
Combining many of these modules allows for a large network of quantum processors that are connected to each other, despite their physical separation from the computer chip.
Bharath Kannan PhD ’22, lead author of the research paper describing the process, says, “Quantum quantum computing is a critical step towards achieving large-scale, modular implementations of machines built from tiny components in the one by one.”
“The ability to communicate between small subsystems will allow a modular architecture for quantum operators, and this can be an easy way to expand the size of a system compared to the hard power of with one big explosion and confusion,” adds Kannan.
Kannan wrote the paper with lead author Aziza Almanakly, a graduate student in electrical engineering and computer science in the Engineering Quantum Systems group at MIT’s Research Laboratory of Electronics (RLE). The lead author is William D. Oliver, MIT Professor of Electrical Engineering, Computer Science, and Physics, Fellow of MIT Lincoln Laboratory, Director of the Center for Quantum Engineering, and Associate Director of RLE.
Quantum information is transmitted
In classical computers, different components perform different functions, such as memory, arithmetic, etc. moving electrons to the computer. But quantum information is more complex. Instead of only having a value of 0 or 1, quantum information can also be both 0 and 1 at the same time (what is known as superposition). Also, quantum information can be carried by particles of light, called photons. These entanglements make quantum information so fragile that it cannot be transmitted solely by means of laws.
Quantum networks are interconnected using photons that travel through special interconnects called wave guides. The direction of the wave can be unidirectional, and move the photon only left or right, or it can be bidirectional.
Most existing facilities use unidirectional wave guides, which are easy to implement because the direction of photon travel is easily adjustable. But since each wave guide moves the photon in the same direction, more wave guides are needed as the quantum network develops, making the process difficult to measure. In addition, unidirectional wave guides often include additional elements to improve directionality, which introduce communication errors.
“We can eliminate these losses if we have a conversion method that can support the spread on the left and right side, as well as a way to choose the direction and the desire. This ‘directional transfer’ is what we have demonstrated, and it is the first step in having high-fidelity two-way communication,” says Kannan.
Due to their structure, many structural modules can be divided into water layers. An outstanding feature of the architectural design is that the same module can be used as a transmitter and receiver, he says. Photons can be sent and received by any two modules in the same normal wave pattern.
“We only have one physical connection that can get any number of modules in the way. That’s what makes it so high. After demonstrating the direction of photons from one module, we are now working to capture downstream photons in the second module,” Almanakly adds.
Take advantage of quantum properties
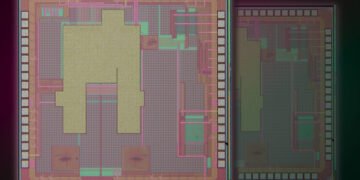
To do this, the researchers built a module with four qubits. Qubits are the building blocks of quantum computers and store and process quantum information. But qubits can also be used as photon emitters. Applying energy to a qubit causes the qubit to become excited, then when it is released, the qubit will release energy in the form of photons.
However, simply connecting a qubit to a wave guide does not guarantee its directionality. A qubit emits a photon, but whether it goes left or right is random. To get around this problem, researchers use two qubits and a property known as quantum interference to ensure that the photons produced travel in the right direction.
The technique is to prepare two qubits in the same excited state called the Bell state. The state of quantum mechanics consists of two parts: the left qubit is excited and the right qubit is excited. Both phases exist simultaneously, but which qubit is excited at any given time is unknown.
When the qubits are in a entangled bell, a photon is transmitted precisely to the wave guide and two qubits at the same time, these two “air paths” canceling each other out. Depending on the relative order in the Bell state, the resulting photon will either go left or right. By aligning the Bell states with the correct order, the researchers select the direction in which the photon travels through the wave guide.
They can use the same method, but on the other hand, to receive photons in another module.
“A photon has a certain frequency, a certain energy, and you can prepare the module to receive it by manipulating it at the same time. If they are not at once, the photon will pass. It’s like tuning the radio on a train station. If we choose the right radio frequency, we will pick up the music transmitted on that frequency,” Almanakly said.
The researchers found that their method achieved over 96% reliability, meaning that if they intended to send a photon to the right, 96% of the time it went to the right.
Now that they have successfully used this system to transmit photons in different ways, the researchers want to connect more modules and use this system to emit and absorb photons. This would be a big step in creating modular structures that combine many tiny operators into a single, larger and more powerful quantum structure.
Yasunobu Nakamura, director of the RIKEN Center for Quantum Computing says, “This work demonstrates the desirable properties of a quantum emitter, in which the interference of a photon emitted from an excited state sets the direction, clearly demonstrates the dynamics of quantum wave guide electrodynamics.” who was not involved in this research. “It can be used as a complete quantum scale that can generate/absorb/transmit/store quantum information over a quantum network and as an interface for a bus connecting multiple quantum computer chips.”