Scientists at Oregon State University are discovering how cells bind together and respond to chemical stimuli in the extracellular environment, an understanding that is critical to understanding health processes and preventing disease processes.
Research by researchers from the OSU College of Science and the Carlson College of Veterinary Science shows that the timing of stimulation plays an important role in the integration of cell communication networks.
Scientists from the University of Pittsburgh have also collaborated in research into what biophysicists call multicellular chemosensing, which is still shrouded in mystery despite its biological importance, according to the researchers. said.
Guanyu Li, a PhD student in the College of Science, said, “We are still far from fully understanding how information networks are regulated by external stimuli or cellular characteristics. “So that’s what our paper is trying to investigate.”
The extracellular environment-which is the fluid that surrounds the cells-has many types of chemicals, Li explains Under certain pathological or physiological conditions, the chemical composition changes and triggers a signal process to occur as the cells create the necessary response maintenance of the normal function.
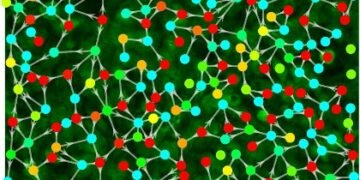
A coordinated response within a cell is made possible by cells exchanging molecules with their nearest neighbors, Li said. The change enables the cells to understand and react to environmental changes better than if they understand and respond to each other and they allow different things to differ. different – people, animals, etc. – to survive in a complex environment.
“For example, when you do cardio training, cells need energy, which will lead to aerobic metabolism to produce more ATP, energy molecules,” he said. “When you’re thirsty, your body produces ADH – antidiuretic hormone – to promote water re-absorption so you don’t die. All these chemical changes are like signals trying to let the body know what’s going on. The receivers of these signals are individual cells.
By binding or binding chemical molecules to receptors on the cell membrane, cells can determine what is happening and trigger the appropriate mechanism. However, the catch is that not all cells have the same ability to bind to these molecules.
“Therefore, in the different organs of each gene, monitoring and response within a group of cells to communicate is very important,” said Li.
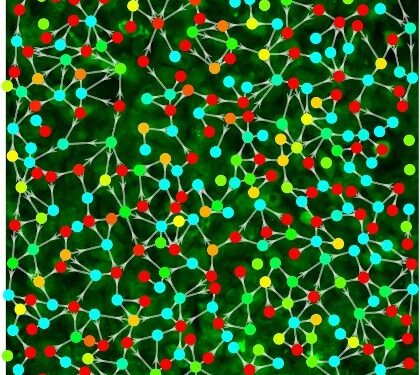
In the study, scientists use statistical analysis to determine the relationship between cells and their nearest neighbors, and conduct research to see the effects of chemical stimuli on cells and networks.
Li, OSU Honors College Alia Starman and associate Professor of Biophysics Bo Sun stimulated brain cells called neurons with ATP, the energy molecule found in all living things. In their experiments, they varied both the amount of ATP in the extracellular space and the length of time the neuron was exposed.
They also experimented with reducing the speed of cell communication using monounsaturated fat, palmitoleic acid, and increasing it with potassium chloride, a metal halide salt.
“Our study shows that the integration of the basic information network is controlled by the temporal profile of the external stimulus – its timing – and the level of communication ability of the cell itself,” said Li. “The dose did not really affect the network. It is also interesting to note that the moderate communication ability of each cell made it the largest link in the cell information network – the maximum communication power or which is less has led to reduced network traffic.
The results shed light on how the networks are organized, opening the door to the possibility of controlling multicellular responses – and fighting disease – through the right kind of stimuli in the extracellular environment, the researchers said.
The study also showed the collective power of even tiny cells, Sun added.
“When you hear music, watch the flashing lights of the car in front of you, or read the waves on the beach, our brain detects the time and predicts when an event will happen and “Next in line will happen,” he said. “But does this work require all the power of the brain? A small system, as simple as a layer of nerve cells, can determine the timing? We have shown that this is possible, and that nerve cells do this by creating and organizing communication networks based on signal feedback.