New research from Cardiff University, in collaboration with Astra Zeneca, has AI created molecules that can carry drugs more efficiently to target and treat patient cells.
The team said their work could have future applications in the treatment of genetic diseases and cancer as well as infectious diseases. Professor Arwyn T Jones, from the School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences at Cardiff University, said: “We are constantly looking for new and better ways to deliver drugs into the human body. Nanoparticles are small particles that can act as microscopic particles to transport and deliver therapeutic molecules – drugs – around the body to reach specific sites that need therapeutic help. “By getting these drug molecules to the right place in the body, nanoparticles can help treat a variety of diseases.”
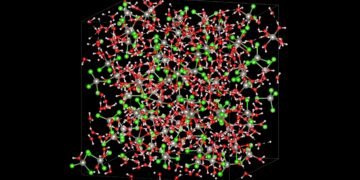
This joint study used AI to design a bespoke nanoparticle to deliver drug molecules, called mRNA, to cancer cells. The AI-designed nanoparticle was later found to be more efficient as a delivery vehicle compared to other forms. “This research has shown that machine learning and artificial intelligence can be an important part of the design process to build more effective nanotherapies.
“Although the nanoparticle produced by this study falls within the narrow field of biomedical research, a new method – based on mathematical learning and the application of a new nanoparticle vehicle – has proven to be effective. This means that this new method can be used to analyze and design thousands of different types of nanoparticles and deliver hundreds of different therapies to target a wide range of diseases,” Professor Jones added.
Nanoparticles are now used in medical treatment, but scientists often make and test hundreds of nanoparticle designs before finding the best one – a process that can take years. This new method shows how AI can accelerate the development of nanoparticles.
“This method provides insight into how cells and cell proteins regulate the performance of nanoparticles as drug carriers. This clearly shows that machine learning can be of great help in the better design of effective nanotherapies to better target and treat diseases,” added Professor Jones.
Source: Cardiff University